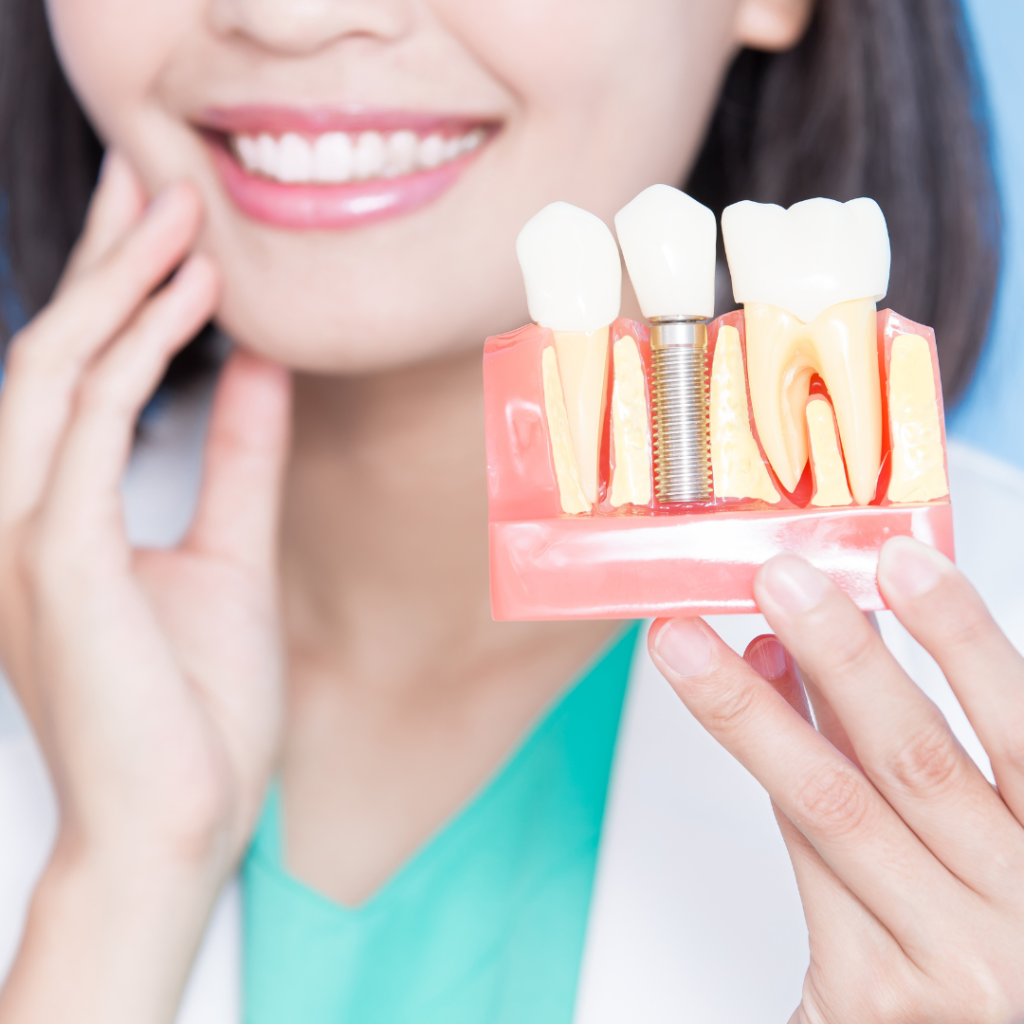
Tooth cyst — effective treatment in Warsaw dentistry
A purulent formation in the jaw bone is not an accidental finding on an X-ray, but a focus of inflammation that gradually destroys the tissues around the tooth root. Under the influence of chronic infection, a cavity filled with pathological contents is formed — this is a tooth cyst. Most often it occurs as a result of pulpitis, poor-quality endodontic intervention, trauma or systemic disorders. In the early stages, the patient does not complain of pain, but a feeling of pressure in the jaw, periodic discomfort, swelling, and a fistula on the gums should alert.
Delaying the treatment of a tooth cyst can result in irreversible consequences. The purulent formation slowly increases, destroying the surrounding bone tissue. As a result, the support of the tooth becomes weak, which leads to its loss. If the cyst breaks through into the surrounding tissues, an abscess, sinusitis and other diseases occur. The infection can spread through the bloodstream and cause inflammation in distant organs — the heart, kidneys, joints. If you do not start treatment of a tooth cyst in time, the cyst can turn into a serious surgical problem with a long rehabilitation period.
Why do patients choose Astra Dent Warsaw for the treatment of a tooth cyst?
It is possible to eliminate cystic lesions without the risk of relapse only with accurate diagnosis and the involvement of doctors specializing in microsurgery and endodontics. The effectiveness of therapy directly depends on how carefully the canals are treated and whether the condition of the tissues is monitored after the intervention. It is important to contact medical institutions that have technical resources and a qualified team to conduct full-fledged therapy with postoperative rehabilitation.
Advantages of treating a tooth cyst at Astra Dent in Warsaw:
- Experienced surgeons and endodontists. The medical center employs specialists with over 15 years of experience in treating complicated forms of cysts. Doctors have been trained according to international protocols and possess modern techniques for root apex resection, retrograde filling and tissue regeneration.
- Modern diagnostics (CT, microscopes). High-resolution computed tomography (CBCT) is used for accurate visualization of the cyst. Endodontic treatment is performed under an operating microscope, which helps to detect additional canals and microcracks that are not accessible during a regular examination.
- Painless treatment. Dentists use the latest generation of local anesthetics, which guarantees the absence of pain during the removal of a tooth cyst. If necessary, treatment under sedation or medical sleep is possible.
- Ukrainian-language support. Patients can count on support in Ukrainian: from consultations to postoperative recommendations. Communication without a language barrier reduces the level of anxiety and allows us to accurately convey recommendations regarding the care of the operated area.
- The possibility of treatment without queues. Appointments are made for a specific time, without long waiting times. In urgent cases, a consultation on the same day is possible.
An individual approach to each clinical case is complemented by detailed diagnostics and a personalized treatment plan, which allows you to avoid repeated interventions and achieve a stable result.
How do we treat a tooth cyst at Astra Dent Warsaw?
The treatment method is determined taking into account the anatomy of the canals, the size and location of the cyst in the jaw. If modern endodontic therapy protocols are followed, the tooth can be saved in more than 85% of cases. Astra Dent specialists make a decision on intervention only after cone-beam computed tomography (CT), which allows you to avoid unjustified removal and determine the most effective approach to treatment.
Stages of treatment
After confirming the diagnosis and analyzing the 3D images, an individual treatment plan is drawn up. Its goal is to eliminate the source of infection, save the tooth (if possible) and prevent the recurrence of cystic formation. The procedures are performed taking into account the clinical situation, the extent of the lesion and the general condition of the patient:
- Endodontic treatment (if possible to save the tooth). The doctor cleans and hermetically seals the canals under microscope control. During the procedure, inert materials (for example, bioactive cements) are used that promote the healing of periapical tissues.
- Surgical removal of the cyst — cystectomy or cystotomy. Cystectomy in Warsaw involves the complete removal of the tooth cyst together with the shell. Cystotomy — partial opening with subsequent drainage and controlled volume reduction. Both procedures are performed using micro-instruments and safe, self-absorbable suture material.
- Root apex resection. If the cyst has formed against the background of chronic inflammation of the root apex, an apicotomy is performed — removal of the affected area with simultaneous closure of the canal from the opposite side.
All stages of treatment are performed on an outpatient basis, in conditions of complete sterility. Thanks to digital planning, the patient immediately receives a prognosis regarding the preservation of the tooth or the need for surgical manipulations.
Anesthesia, safety, recovery
Interventions are performed on an outpatient basis, with an emphasis on the comfort and safety of the patient. Even the most delicate procedures do not cause pain, thanks to effective methods of anesthesia and structured postoperative support:
- Anesthesia. Modern anesthetics with high diffusion capacity are used, which block pain even in hard-to-reach areas. The drugs are almost not injected into the cardiovascular system, which is extremely important for patients with chronic diseases.
- Drug therapy. After surgery, antibiotics, anti-edema agents and, if necessary, painkillers are prescribed. The drugs are selected individually.
- PRF technology. In cases of bone tissue damage, platelet-rich plasma injections (Platelet-Rich Fibrin) are used, which accelerate healing and stimulate regeneration.
A separate set of sterile equipment is prepared for each patient. All contact areas in the office are disinfected with antiseptics after each appointment. A set of disinfection measures reduces risks during the intervention and guarantees controlled recovery after cyst treatment.
Postoperative care
Astra Dent patients receive a clear, personalized rehabilitation plan immediately after cyst removal. Doctors explain each stage of recovery and leave written instructions.
Standard recommendations after cyst removal or resection:
- Hygiene. During the first 5 days, avoid mechanical trauma to the intervention site. Brushing teeth with a soft brush, without contact with the postoperative wound. Rinsing — only on the recommendation of a doctor (antiseptic solutions or saline, not earlier than after 24 hours).
- Nutrition. Avoid hot, hard, spicy food. In the first two days — only soft, warm dishes. Alcohol, smoking and coffee should be excluded for at least 5-7 days.
- Medical support. It is mandatory to take antibiotics (if prescribed), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and, if necessary, painkillers.
- Physical activity. During the first 48 hours, limit the load, do not tilt your head down, avoid sports, saunas and hot baths.
- Cooling the area. During the first 6-8 hours, it is recommended to apply cold (through a cloth) for 10-15 minutes with breaks.
Following the recommendations reduces the risk of complications. In case of discomfort or changes in condition, the patient can contact the doctor directly: Astra Dent provides postoperative support without time limits.
Diagnosis of a tooth cyst at Astra Dent Warsaw
The initial stages or atypical location of the cyst may go unnoticed during a standard examination. To avoid diagnostic errors, Astra Dent specialists use additional imaging methods that allow assessing the three-dimensional structure of the lesion.
How a tooth cyst is diagnosed at Astra Dent:
- Examination by a dentist. A detailed examination of the condition of the mucous membrane, gums, percussion (tapping) of the teeth, a sensitivity and probing test is performed. The doctor assesses possible external manifestations — swelling, discoloration, fistulas, and also clarifies the patient's complaints and history.
- X-ray or CT scan of the jaw. Targeted radiography reveals the boundaries of the cyst, its relationship with the root and the condition of the filling. If three-dimensional visualization is required, CBCT is performed — computed tomography, which shows the depth of the lesion, proximity to the maxillary sinuses and nerve canals.
- Clarification of the size, localization, and condition of bone tissue. Based on the images obtained, the doctor analyzes the extent to which the infection has affected the bone, whether there is a risk of inflammation of adjacent structures. Depending on the results, an individual treatment plan is drawn up.
Astra Dent specialists use a fully digital approach: the images are immediately integrated into the patient's electronic card, and the decision on intervention is made on the basis of objective data. As a result, the likelihood of error and unnecessary manipulations is reduced.
What is a tooth cyst
A tooth cyst is a hollow formation in the bone tissue of the jaw, filled with fluid or pus and covered with a dense membrane. It occurs as a complication of prolonged inflammation in the area of the tooth root, and has a tendency to grow slowly. The formation gradually destroys the surrounding bone, but may remain asymptomatic until it significantly increases in size.
Usually, the cyst is localized near the apex of the root of the affected tooth or around the unerupted crown. On an X-ray or CT scan, it looks like a rounded darkening with clear boundaries. Manifested by pain, swelling, fistula or facial asymmetry, especially with secondary infection.
Types of cysts:
- Radicular. The most common type that occurs due to chronic inflammation due to pulpitis or poor-quality root canal treatment.
- Follicular. Formed around the crown of an unerupted tooth, most often in the area of the lower third molar (wisdom tooth).
- Residual. Formed at the site of a previously removed tooth, if the tissues were not completely cleaned.
- Paradental. Occurs next to partially erupted teeth, mainly near the lower molars, as a result of local inflammation.
- Keratocyst (odontogenic). Atypical form with an increased risk of recurrence, sometimes has a genetic nature.
Accurate determination of the type of cyst is important for choosing treatment tactics. For this purpose, a full range of diagnostic procedures is used: 3D scanning and, if necessary, histological examination after removal of the purulent cavity.
Causes of cyst formation
Cystic formations are the result of a long-term pathological process that can remain unnoticed for years. Cyst formation is associated with a chronic infection in the root area of the tooth, which was not diagnosed or properly treated in time. The accumulation of bacteria triggers an immune response, as a result of which the body "isolates" the affected area, forming a capsule. Cyst formation can be caused by a number of factors:
- Complicated caries. Deep damage to the hard tissues of the tooth opens the way for infection to the pulp. If the process is not stopped, bacteria penetrate the root canals, provoking inflammation, which subsequently transforms into a cyst.
- Untreated pulpitis or periodontitis. Incomplete removal of the affected pulp or insufficient filling of the canals creates conditions for chronic inflammation around the root. Over time, it turns into a slow destructive process with the formation of a cyst.
- Complications after injuries or improper filling. Mechanical damage to the tooth (crack, dislocation, chip) or excessive pressure on the periapical tissues with an improper filling can lead to impaired blood supply and inflammation in the root zone.
- Genetic factors. Certain types of cysts, in particular odontogenic keratocysts, are hereditary in nature. They occur without an infectious factor, as part of systemic syndromes or in isolation, against the background of genetic mutations.
During diagnosis, Astra Dent specialists necessarily take into account the patient's history, imaging data and history of previous treatment, which allows preventing the recurrence of the cyst.
Symptoms of a tooth cyst
The initial stage most often goes unnoticed by the patient. The capsule grows slowly, without causing pain or external changes. It is often detected by chance during an X-ray examination. If a cyst is suspected, Astra Dent doctors perform a diagnosis, even if the symptoms are absent or minimal.
In which cases should you consult a dentist:
- Gradual pain, swelling, discomfort. As the formation grows, dull pain appears when touching the affected area, pressure under the tooth or slight swelling of the tissues. In some cases, discomfort appears only when chewing or when the temperature of food changes.
- A feeling of pressure or distension. Patients describe this as "tension in the bone", which does not go away even at rest. It is due to the fact that the cyst gradually presses on the surrounding structures.
- Visible flux, fistula. In case of exacerbation, swelling of the gums, an abscess or a channel through which the contents are released (fistula passage) occurs. This is already a complicated form that requires urgent care.
Early detection of a cyst increases the chances of conservative treatment without surgical intervention. For this purpose, Astra Dent has implemented a system of mandatory X-ray diagnostics at each initial examination, which detects hidden foci of inflammation even before symptoms appear.
What is dangerous about a cyst
Ignoring the problem creates the risk of systemic disorders. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), untreated cysts become a source of serious consequences — from acute infections to bone tissue damage:
- Can lead to tooth loss. The development of a cyst is accompanied by a slow thinning of the bone around the root. If it is not stopped, the tooth loses stability, becomes mobile and cannot be restored after root canal treatment.
- It grows, destroys the bone. The cystic formation exerts pressure on the surrounding bone structure, causing its gradual resorption. The defects formed can be so significant that without prior osteoplasty, the installation of a dental implant becomes technically impossible.
- Puts at risk neighboring teeth. If left untreated, the cyst expands towards other roots, causing secondary inflammation, atrophy of the supporting tissue and increased mobility of adjacent teeth.
- Can become a source of infection for the entire body. In the event of a breakthrough or exacerbation, purulent contents enter the surrounding tissues or bloodstream, which threatens sepsis, lymphadenitis, thrombosis of the facial veins.
The longer the patient postpones treatment, the wider the scope of the lesion. The infection penetrates neighboring tissues, creating complex combined defects. In such cases, recovery requires reconstructive treatment — from bone grafting to orthopedic rehabilitation.
How to make an appointment at Astra Dent Warsaw?
Have you detected symptoms of a cyst or do you want to undergo diagnostics before installing an implant? Astra Dent in Warsaw is staffed by specialists who work according to international protocols for the treatment and diagnosis of jaw tumors. You can make an appointment in one of the following convenient ways:
- by phone: +48 533 599 55;
- by e-mail: info@astradent.pl;
- via the website: fill out a short form on the official website.
The dental center is open every day — from 9:00 to 20:00 on weekdays and from 9:00 to 18:00 on weekends. A preliminary appointment allows you to avoid queues, and the consultation is held at the exact time specified. If the question concerns pain, swelling or suspicion of a cyst, an appointment is possible in the next few hours.